How to white balance Nikon cameras
Why do a preset white balance?
The cameras made today are extremely sophisticated and they can judge pretty accurately what kind of photograph is being shot under what lighting conditions. But sometimes, you need to give them a little push so that they are able to serve you better. If you feel that your photographs are too warm or too cool for your taste, maybe it is time for you to do a custom white balance or as Nikon calls it - preset white balance. We are going to take a look at the easiest, cheapest and fastest way to white balance Nikon cameras. If you want to know about custom white balance on Canon cameras, please read this article here.

White balance is nothing but getting rid of the colour casts on your photographs by telling the camera, "Hey! This is white! Please make other adjustments accordingly!" So logically, the easiest way of doing this is by showing the camera a piece of white paper and telling it that this is white. Different cameras have different ways of measuring white under different lighting conditions, though internally the process remains the same.
How to white balance Nikon cameras
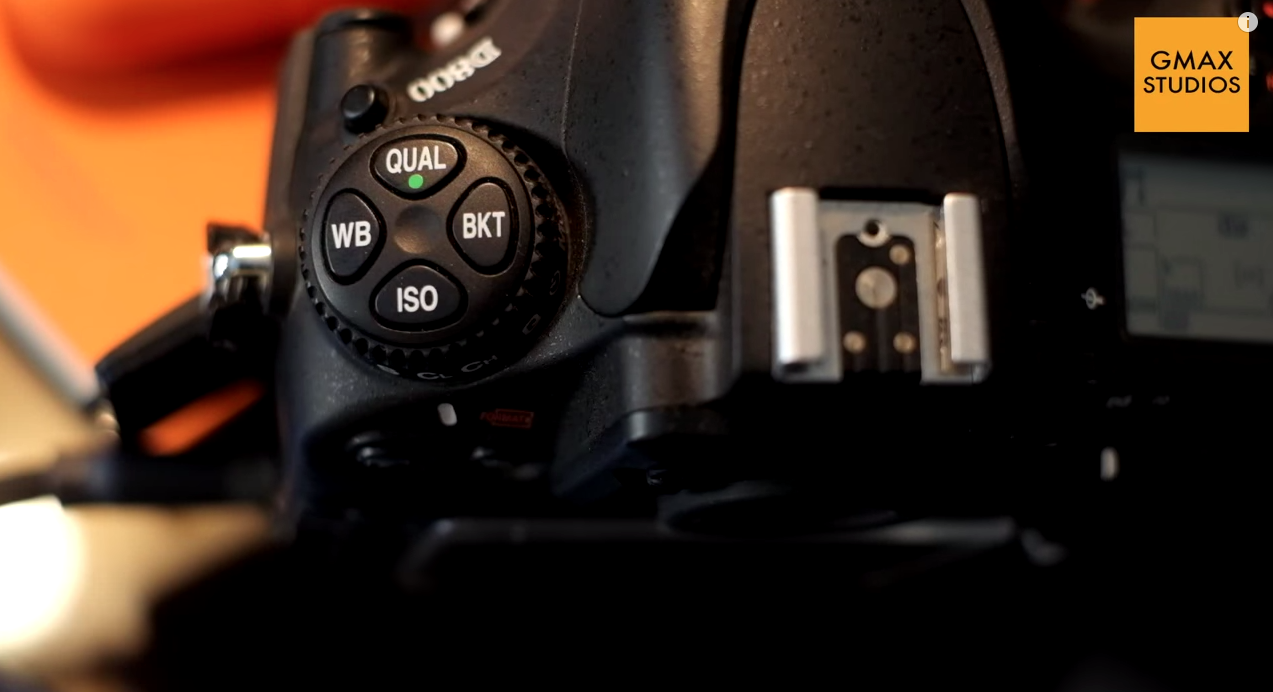
Nikon calls this adjusting the PRESET white balance and it is done by pressing the WB(white balance) button on the camera and turning the command dial until the display show "PRE". You then release the WB button and press it again. The PRE now begins to flash. This means that the camera is in ready mode to take the new white balance setting. Now all you need to to do is put a white paper in front of the camera and press the shutter button while the PRE is still flashing. The display should read "GOOD" which means your preset white balance was successful.
Important
- The white paper should fill the entire frame - nothing else should be visible.
- If you are shooting a wide shot, zoom in to the white paper or move closer to the paper.
- Do not get the paper close to the camera as the light falling on the paper has to match the light falling on your subject. Get the camera closer to the paper instead.
- If the camera is hunting for focus, switch to manual focus. It will not make a difference if the paper is out of focus to take the white balance reading.
- If the camera displays "NO GOOD" that means that the camera was unable to get a proper reading. Check if your exposure is correct. Underexposure or over exposure might cause a bad reading.
- Make sure that the PRE is flashing when you press the shutter button.
Please watch the short video below to understand this process better. If you have any questions, please ask them in the comments and if you like the video, please subscribe to our channel by clicking here.
https://youtu.be/CL_WPm13zI0
Please ask any questions that you might have in the comments section below.
Photography | Shooting in manual mode
Shooting in manual mode
Shooting in manual mode is made out to be something really, really BIG. It's as if you are not a true photographer until you shoot in manual mode. Nothing could be further from the truth. Each mode on the camera whether it is aperture priority, shutter priority, program mode or manual mode has got a specific use and a smart and good photographer knows when to use them.

Why shoot in manual mode?
The question that many people ask is - why shoot in manual mode at all when the average camera has such sophisticated technology built into it that it is almost guaranteed that you will get a perfect exposure every time? Shooting in manual mode has it's benefits. One very basic thought behind shooting in manual mode is that it really helps you understand the process of taking a photograph. In that sense, it makes you a better photographer.
Once you are familiar with the way a photograph is made and you understand the reason why a photograph turns out the way it does, it will be easier for you to shoot in other modes as well. Also, it has the benefit of being able to replicate the look and feel of the photographs that you like. A great example of this is people who shoot portfolios in the studio. Once they have figured out the look they want, they know exactly what settings to shoot on rather than mess with them each time a new client walks in.
I personally use the manual mode when I don't want the camera making too many decisions on my behalf. This usually happens when I come to a setting where I am happy with the exposure - both on my subject and the foreground (if any) and the background and I am not expecting the light to change too much. This might happen while shooting with flash or in natural light. In natural light though, you will have to keep checking the exposure at certain intervals to ensure that the moving sun has not caused any change in the desired exposure.
Usually the camera tries to act smart and changes the exposure value if you recompose - like move the subject to one side of the frame or zoom in etc. This is what I don't want happening. Once I am happy with the exposure, I am happy with it. That is why I use the manual mode to lock it down.
How to shoot in manual mode?
In manual mode, you take over all the controls from the camera, which is aperture, shutter speed and ISO. You do this my switching to the M mode on the camera.
- You define your starting point by deciding what is more important to you - the aperture or shutter speed.
- The ISO obviously is at the lowest setting when you start off and this will be the last thing that you increase.
Watch the video below to understand how to nail and lock down shooting in manual mode. It is no rocket science - I can definitely assure you of that. Subscribe to our channel if you feel like it by clicking here.
http://youtu.be/Hv3UXdxSxrM
What is white balance in photography and how to master it?
What is white balance?
Most of the time, most of the people set their cameras to automatic white balance and forget about it and sure enough, for most of the people this seems to suffice and they get decent enough pictures to suit their purpose. This is due to the great advances in technology that we seem to have made over the past few years. If you want real control over the kind of pictures that you take, you have to stop relying on technology and what the camera asks you to do. To take pictures where the colour is finely controlled by you and nobody else you have to master some basic techniques. White balance is one of them.
White balance (WB) is the process of balancing the colour in your photographs, so that objects which appear white in person are also white in your photographs. Our eyes are very good at judging what is white under different lighting conditions - like the yellow light emitted from our bulbs at home or the white light emitted from the tube lights we use, but digital cameras often have difficulty in "seeing" under these lighting conditions. Even daylight for that matter changes its colour at different times of the day. You definitely must have noticed that sunlight has a warm glow in the morning and evening which is missing during the day. The sunlight appears quite bright, harsh and white during midday. To understand this better let us figure out what is the difference between warm, cool and neutral tones.
Understanding tones
WARM TONE IN A PHOTOGRAPH
Any photograph that has red or orange tones on it is said to be "warm". This is usually due do some warm light - like a bulb or the evening sunlight falling on the subject.
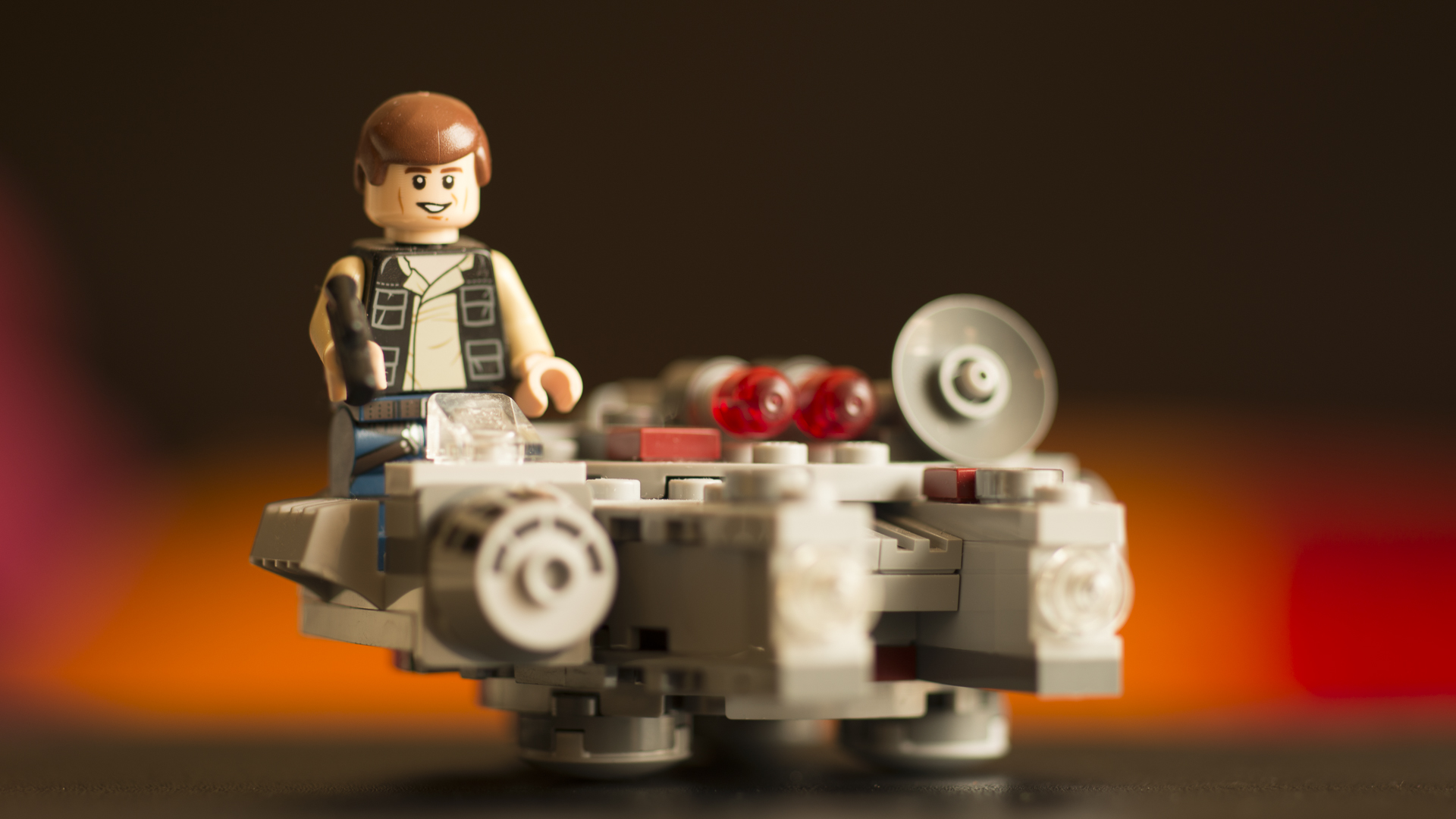

COOL TONE IN A PHOTOGRAPH
If a photograph has a bluish tint to it, it is said to be "cool". This usually happens if you photograph subjects in shade, away from the sun or after sunset during the evening.
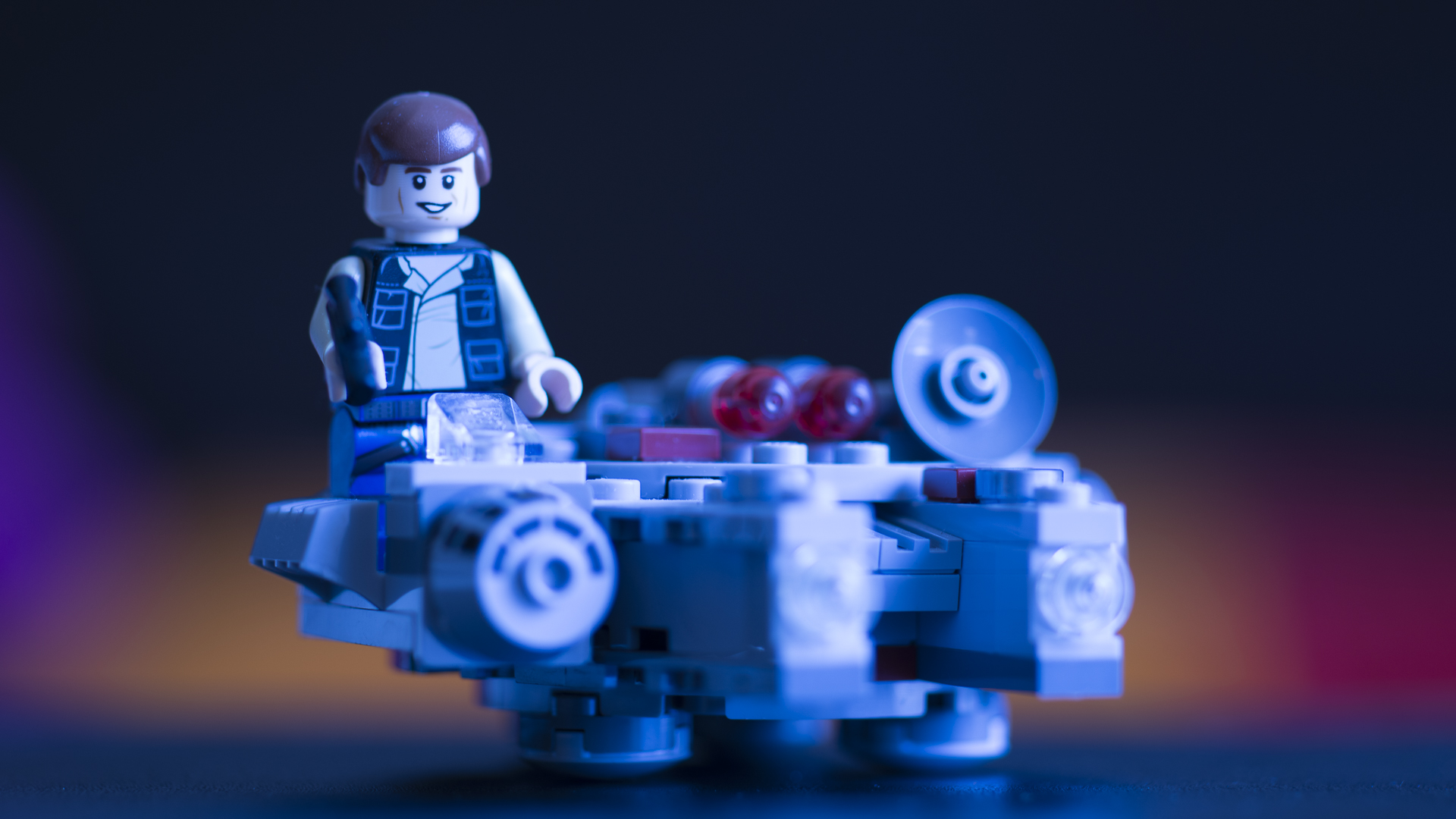

NEUTRAL TONE IN A PHOTOGRAPH
If a photograph is neither warm nor cool, it is said to be neutral. An important point about neutral photographs is that the colours in it are true. They appear to exactly the way they are, in real life.

The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source. Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing,astrophysics, horticulture, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is only meaningful for light sources that do in fact correspond somewhat closely to the radiation of some black body, i.e., those on a line from reddish/orange via yellow and more or less white to blueish white; it does not make sense to speak of the color temperature of, e.g., a green or a purple light. Color temperature is conventionally stated in the unit of absolute temperature, the Kelvin, having the unit symbol K.
- Most DSLRs have a colour temperature range of between 2500k and 10000K
- In your camera, the lesser the number (closer to 2500K) the cooler your photograph will be and the larger the number (closer to 10000K), the warmer your photograph will be. Absolutely white light is measured at 5600K.
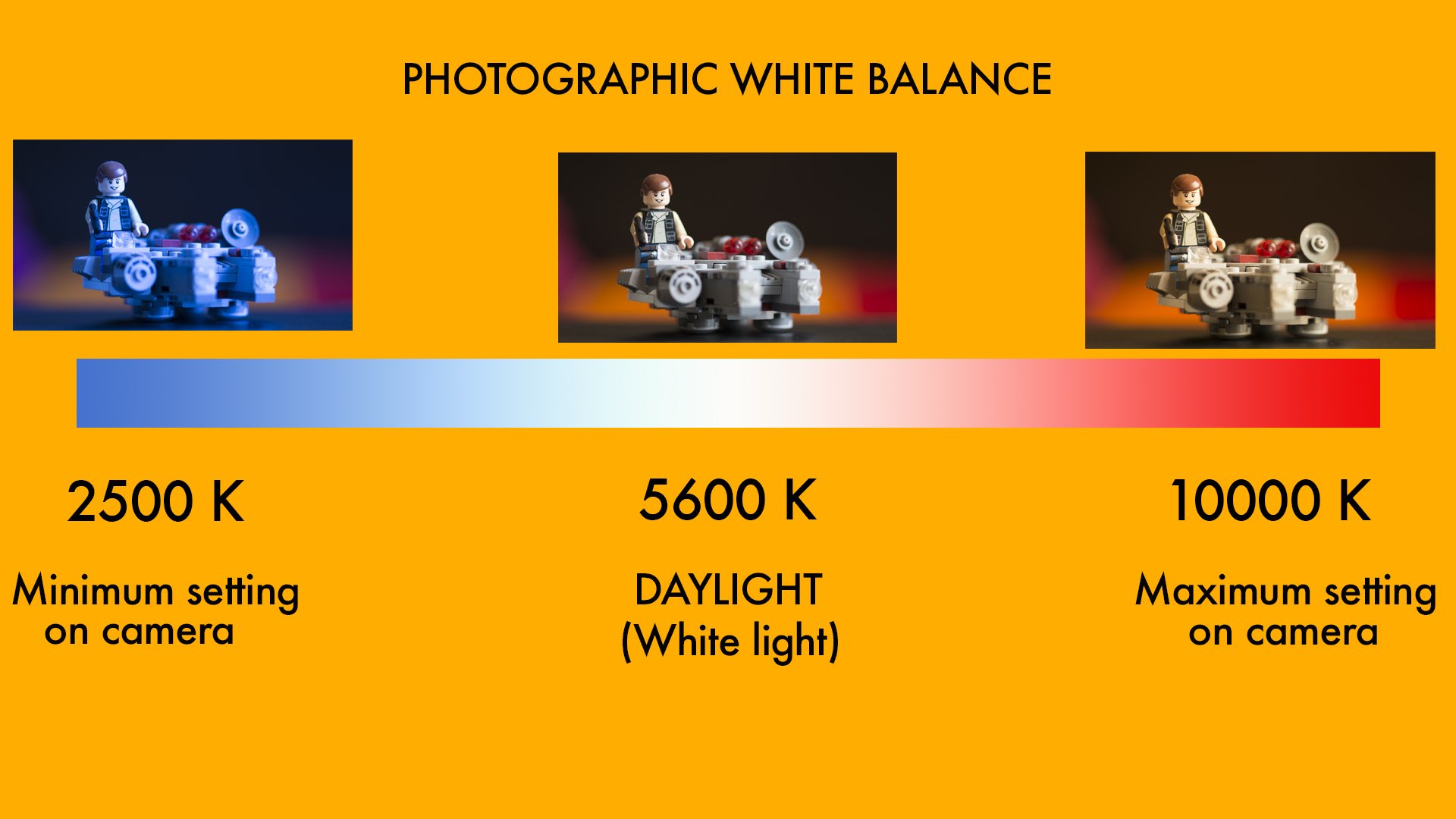
In my opinion, pure white light does not exist naturally. It can only be seen from man made light sources like professionally made HMI lights like they use on film sets or from flash(strobes) used in photography or LEDs. Natural light sources always have a tone to them.
How to set white balance on your camera?
There are three ways that you can set white balance on your camera.
- Auto white balance: As said earlier, auto white balance or AWB gets the job done 90% of the time and in the newer cameras it is pretty accurate or even amazing at times but with the camera set to auto white balance (or AWB) — your photographs can end up looking slightly blue, orange, or even green.
- Using the built-in settings: This involves figuring out what kind of light your are shooting under and matching it with the appropriate setting in the camera. So if you are shooting in sunlight, you choose the "sunlight" white balance setting on the camera (symbolised by a "sun") and if you are shooting in cloudy lighting conditions, then you use the cloudy settings and so on. This method too works well - but just barely. It is not very accurate and differs between camera brands and models.
- Using a custom white balance or preset white balance: This is the most accurate method of making sure that you get an absolutely neutral photograph and true colours.White balance or setting colour temperature is you telling the camera that under these lighting circumstances which colour it is to assume is “true white". Once you tell the camera that under these lighting circumstances, THIS is white- the camera is smart enough to make the necessary adjustments to render all other colours the way they are.The easiest way of doing this usually involves putting the camera in custom white balance mode and "showing" the camera a white sheet of paper and then taking a picture with it. What this does, is that it tells the camera that - "this is white" under these lighting conditions. Once the camera understands that, it makes all the other adjustments accordingly and all your colours come out looking just the way they should. You can use a device like Expodisc too, instead of the paper which will make the results more accurate.
If you shoot RAW, you can also, take your photographs to Adobe Lightroom or Photoshop and make corrections to the colour temperature in these programs. You can watch the video below to understand more about white balance and how to set it correctly. You can also read the articles (links under the video) on how to white your Nikon or Canon specifically.
Important
While understanding white balance can help you avoid these unnatural tones and improve your photos under any lighting condition. It is not a rule that you must have absolutely neutral tones for each and every photograph you take. You might prefer a warm or cool tone and that is perfectly alright. In fact, skin does look better in a slightly warm tone and many photographers deliberately "warm up" their photographs to make their subjects look better.
https://youtu.be/buex57O_Q5U
Also see:
How to set custom white balance on Canon DSLRs
and
How to set preset white balance on Nikon DSLRs
What is ISO in photography?
What is ISO in photography? In times when people used film cameras to take photographs, ISO sensitivity expressed the speed of photographic negative materials and it used to be expressed as ASA. But now, since digital cameras do not use film but use image sensors instead, the ISO equivalent is usually used.
What ISO denotes is how sensitive the image sensor is to the amount of light present. The higher the ISO, the more sensitive the image sensor is to the available light. So if you are shooting in low light conditions, you need to increase the ISO. Most cameras have 100 ISO as their lowest setting.
When people used film, they usually had to change the roll of film to change their ISO. It was not uncommon for people to carry two different cameras with two different rolls of film - each with a different ISO in order to shoot under different situations. The lower ISO 100 film would be used for shooting in daylight and the higher ISO, 400 and above would be used to capture night scenes.
Now you just need to change your ISO within your camera from a lower to higher setting to be able to take night shots.
Caution
Having this great feature in your camera can be quite powerful but be careful, shooting at high ISO can cause noise to appear in your photographs. This can be seen in the photographs below.
ISO in photography
The above image was shot at ISO 100 and as you can see there is hardly or no noise. The image below was shot at ISO 3200 to illustrate how noise can appear at higher ISO settings. Each camera has it's own noise threshold, so make sure you test your own camera before you increase the ISO levels.
What is ISO in photography
Watch this video to understand more about ISO and please remember to subscribe to our channel by clicking here.
Please share this post with your friends if you found it helpful.
Understanding shutter speed in photography
Understand shutter speed in photography
The shutter speed, is essentially the time or the amount of time that the shutter remains open to allow light in. It is usually expressed in fractions like 1/60, 1/120, 1/250 etc which basically means that the shutter remains open for the 60th of the second, 128 of the second or 250 of a second.
The longer the shutter remains open, the more the light enters the camera and hits the film or the sensor and the shorter the duration of the shutter the lesser the light which enters the camera. It is almost like turning a tap on or off. The longer the tap remains open the more the water in the bucket.
An important point to note in this, is that, as fractions go 1/120 is actually a longer period of time than 1/250. If you are as hopeless with fractions as I am, just remember–the higher the number, the faster the shutter speed. By this logic, 1/1000 is faster than 1/500 which is faster than 1/250 and so on.
shutter speed
Also, what needs to be remembered is that once the shutter speed goes below one second, you will begin to see a quotation mark in front of the number which actually means “second". So the shutter speed of one second will be expressed as 1" and a speed of two seconds will be expressed as 2".
A " next to the shutter speed denotes that that speed is in seconds instead of a fraction. 2"
means that the shutter speed is 2 seconds and not 1/2 second.
Using slow or fast shutter speed
If we assume that the aperture is constant, when you slow down the shutter speed, you are letting in more light because your shutter stays open for a longer time. The opposite happens when you increase your shutter speed. Both, a slower shutter speed and a faster shutter speed have different uses and can be used creatively to capture different kins of photographs.
Using slow shutter speed
As said earlier, slowing down the shutter for a longer period lets in more light but there is another thing that happens.
Slow shutter speed also gives time for the object you are shooting - the time to move, thereby inducing a "movement blur" in the photograph.
While nobody wants blurry photographs, if you can control the blur it gives a lot of opportunity to explore your surroundings creatively.
A classic example of this is the photograph below. The camera is on a tripod and a long shutter speed has been used.
slow shutter speed in photography
The camera has been put on a tripod to ensure that there is no camera shake. Hand holding the camera when the shutter speed is slow might cause your hand to shake and the whole photograph will turn out to be blurry.
Since the rocks are stationary, they appear sharp.
Since the water is moving, the slower shutter speed causes a blur in the water - giving it a milky feel.
During the day, you might not be able to slow down the shutter speed enough to achieve this effect and you might need a Neutral Density filter to slow down the shutter speed.
Here is another example of using a slow shutter speed.
Slow shutter speed in photography causes objects to blur
Using a fast shutter speed
Using fast shutter speed allows you you to freeze motion. Usually, you don't need a tripod to shoot at very fast speeds because there is very little possibility of your hand shaking. All those sports photographers you see on the sidelines? They are mostly shooting at very high shutter speeds to freeze the action - and their tripods are usually there to support the heavy "mother of all zoom lenses" that they are using.
Fast shutter speed
The photograph above is a complete contrast to the photograph of the waterfall that we saw earlier. Here, due to the fast shutter speed, the water appears to be frozen in time. We can almost see each droplet with clarity.
Here is another example.
Using fast shutter speed in photography
The graphic below sums up how this all works.
shutter speed photography definition
Also watch the video below to understand this better.
Also read:
How aperture affects the look of your photographs and depth of field
Please share this article with your friends on Twitter, Facebook and Google Plus if you found it useful and leave us a comment if you have any questions.
Understanding aperture in photography
Understanding aperture in photography
Imagine in your mind, how the camera works. For you to make a good photograph, a certain amount of light needs to hit the sensor. Let us assume this amount of light to be hundred units. If the light hitting the sensor lesser than the amount of light required, the photographs will be dark or “underexposed”. Similarly, if the amount of light hitting the sensor is more than the amount of light required, the picture will be over-bright or “overexposed”.
There are two ways of controlling the amount of light hitting the sensor-via the aperture or with the shutter speed.
What is aperture?
The aperture is nothing but the hole in the lens through which the light enters the camera. For the time being, all you need to know about the aperture is that smaller the number [1.4 or 1.8], the bigger the aperture and similarly, the larger the number will [16 or 22], the smaller the aperture or the size of the hole on the lens.
Understanding aperture in photography
All these numbers are often referred to by using the alphabet F in front of them. So 1.4 is referred to as F1 .4 and 16 is referenced to as F-16. This is just another way of trying to sound cool. There is actually no difference if you say 16 or F-16.
Understanding aperture in photography - Aperture closed down
Just remember, the smaller the number-the bigger the whole AND the bigger the number, the smaller the hole. This is all that you need to remember about the aperture. This will become second nature as time goes by but it is crucial that for the time being, you remembered this!!!
Understanding aperture in photography - Full open aperture
The size of the aperture is measured in f-stops, which control the depth of field. With few exceptions, each f-stop lets in half as much light as the next larger opening and twice as much light as the next smaller one. From the largest opening to smallest, standard f-stops are as follows: f/1, f/1.4, f/2, f/2.8, f/4, f/5.6, f/8, f/11, f/16, f/22, f/32 and f/45. This can be a little confusing because the larger the f-stop, the smaller the amount of light that is let into the camera. The easiest way to think off-stops is in terms of fractions: just as '/i6 is less than l/s, an f-stop of f/16 is smaller than, and lets in less light than, f/8.
You won't find the full range of settings on any one lens. In most cases, the standard lens on a digital camera is in the f/3.5—f/16 range.
The maximum aperture of a lens determines by how much it can be opened. The maximum aperture is also referred to as the maximum iris, or the speed of a lens. Although lenses are referred to by their focal length, the description of a lens also carries a second number, such as 2.0 or 3.5, which indicates the maximum aperture of the lens. Larger maximum apertures, such as f/1.8, let in more light than smaller apertures, such as f/3.2, allowing you to take better shots in low-light situations.
Watch the video below to understand aperture better.
Also read: How aperture affects your photograph - Depth of field
Please share this post with your friends if you found this useful.
Learn photography by reading: The Ultimate Photography Guide for Beginners
How is a photograph made
How is a photograph made?
When taking a picture, you press the shutter release and there are two things that happen:
- The shutter opens for a fraction of time to let light from the scene to be focused onto the image sensor. The fraction of time for which the shutter opens is called shutter speed.
- The light coming in comes through a hole in the lens. This hole is called an aperture - an adjustable opening that regulates how much light passes through the lens.
So, to get the ideal exposure, just the right amount of light must strike the image sensor. If there is too much light - your picture will be overexposed and if there or too little light, your picture will underexposed. In either case you need to adjust the amount of light coming into the camera. So we can do this one of two ways:
- Change the shutter speed. Make the shutter speed slower (so that it remains open for a longer time) to allow more light to come in OR make the shutter speed faster to let less light come in - depending upon whether the photograph is under or overrexposed.
- Another way to change the amount of light coming into the camera is by opening or closing the lens's aperture. 'Stopping down' the aperture makes it smaller so that it lets in less light. Opening it up lets in more light.
http://youtu.be/vZ-_zMSqnKk
Once the right amount of light hits the sensor or film - you will have the perfectly exposed picture.

Please subscribe to our channel if you like the video by clicking here or click on the image below to watch all our episodes on photography.
Also please don't forget to leave us a comment if you have a question or would like to leave a request as to which video would you like to see next.
How aperture affects photos |Depth of field
When you learn photography, it is easy to get confused between the various modes on the camera.
I shoot on A aperture priority mode on my camera 99% of the time (see Aperture).The main reason I do this is because I don't shoot too much of action and sports and thus find no reason to switch to S, shutter priority mode. I also like to control my depth of field or DoF as it is known. In easy terms, depth of field refers to how blurred out your background is, compared to the focus point. This is controlled by the aperture.
How aperture affects photos - Depth of field
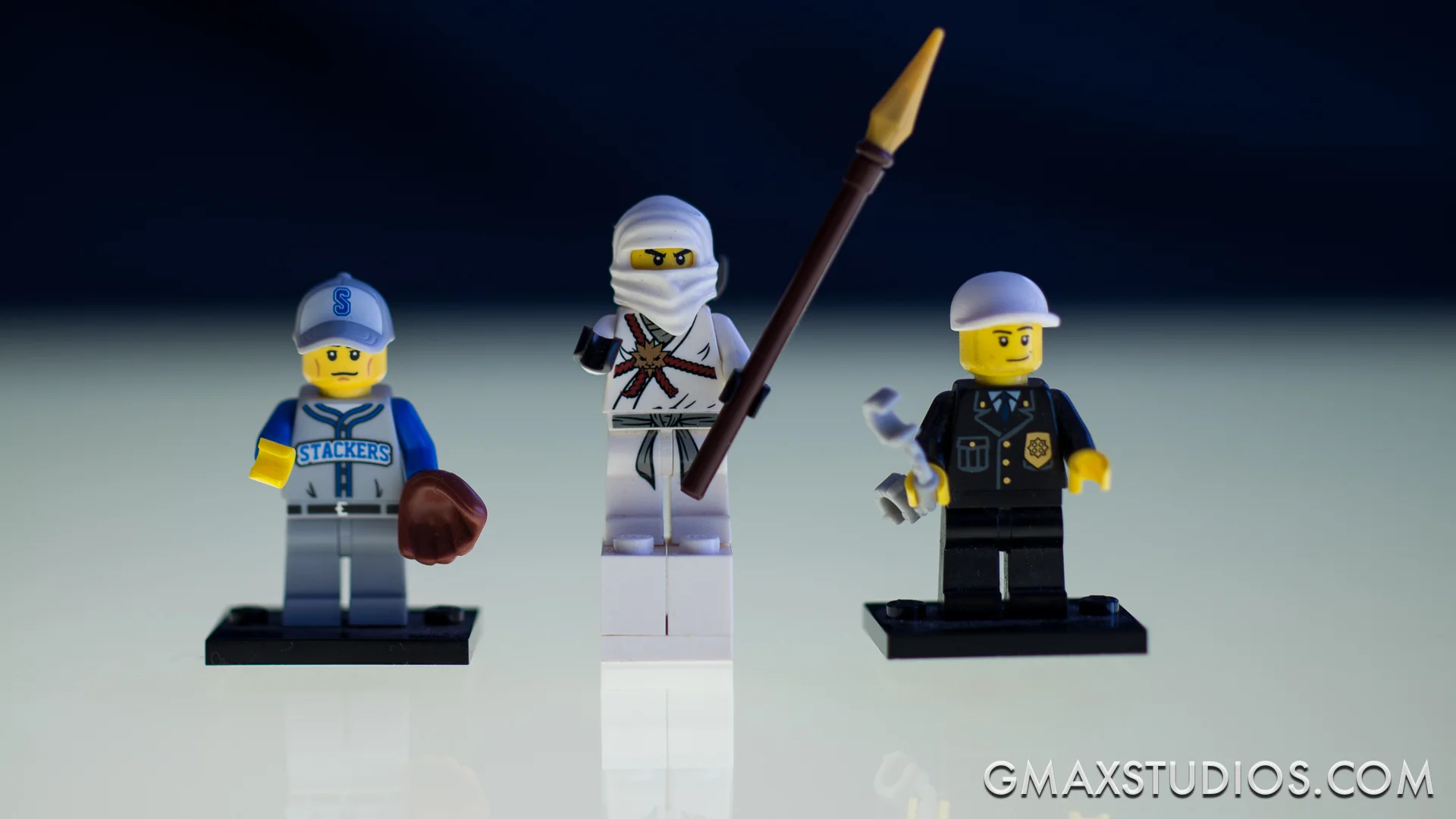
To demonstrate this point, enter "The GMAX Team":
I shot the image below on an aperture setting of 1.8 on my camera. The camera automatically set the shutter speed to 1/160th of a sec.
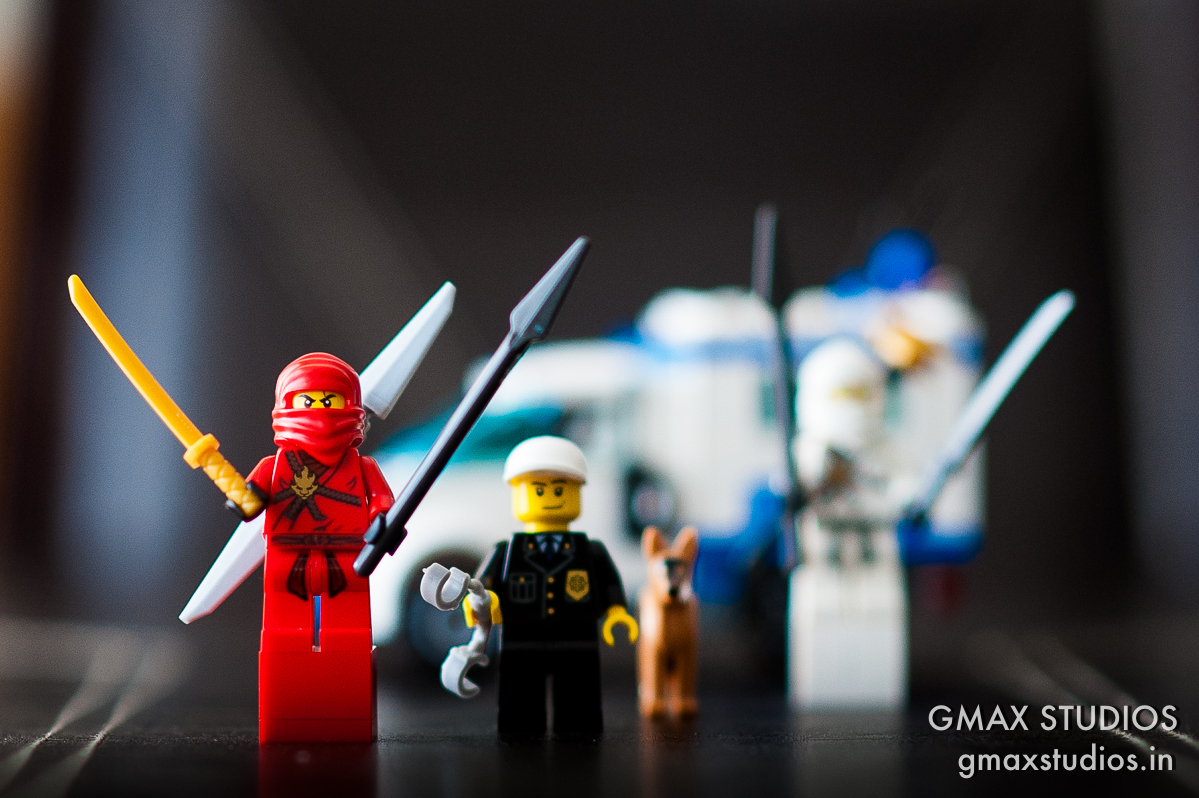

The focus is on Kai, the red Ninja. Notice, that though the difference between the team members is only inches - they have been arranged slightly one behind the other - the policeman, appears to be blurred. The focus gently blurs from Kai, to the policeman's handcuffs and the dog Tommy and Zane, the white Ninja are completely blurred.
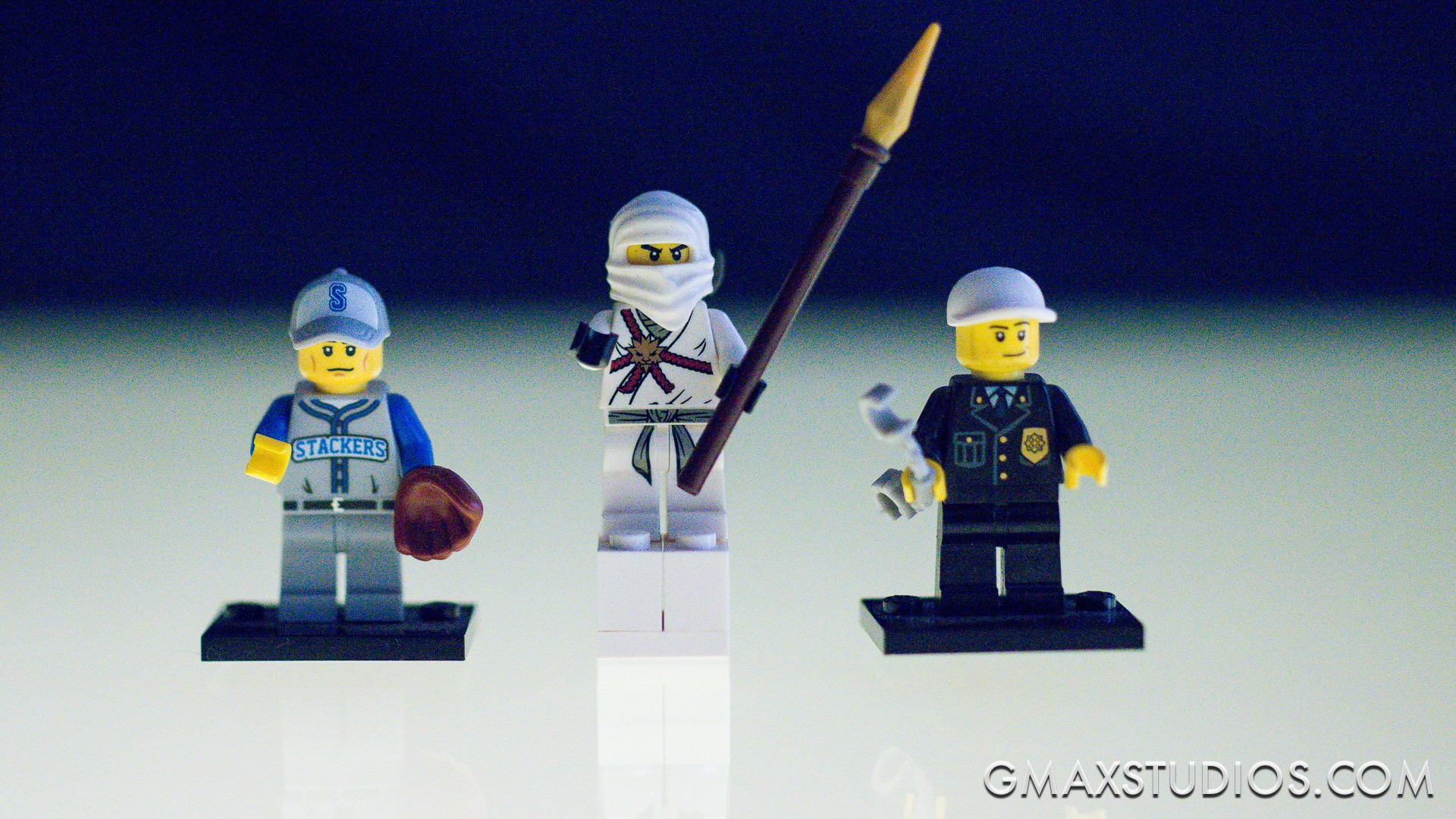
For the next shot I changed the aperture setting to f4. The background is gradually beginning to come in focus. The policeman is happy now.
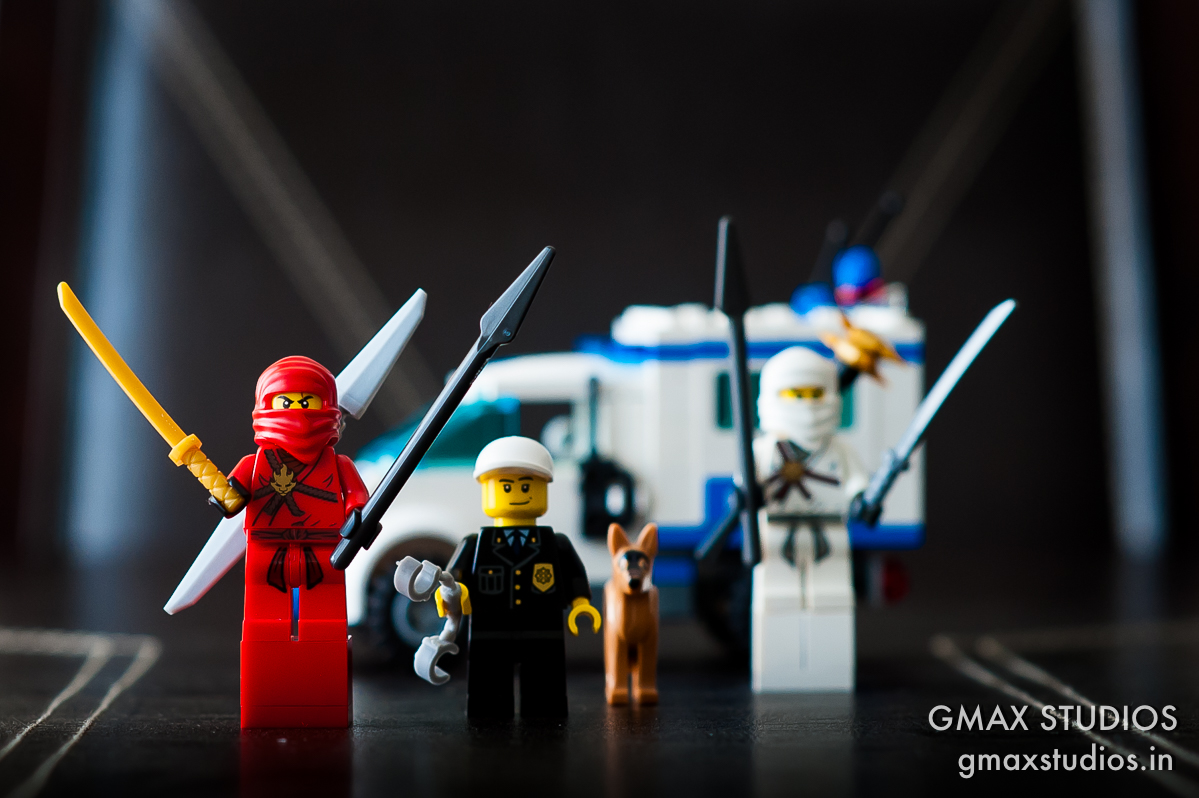
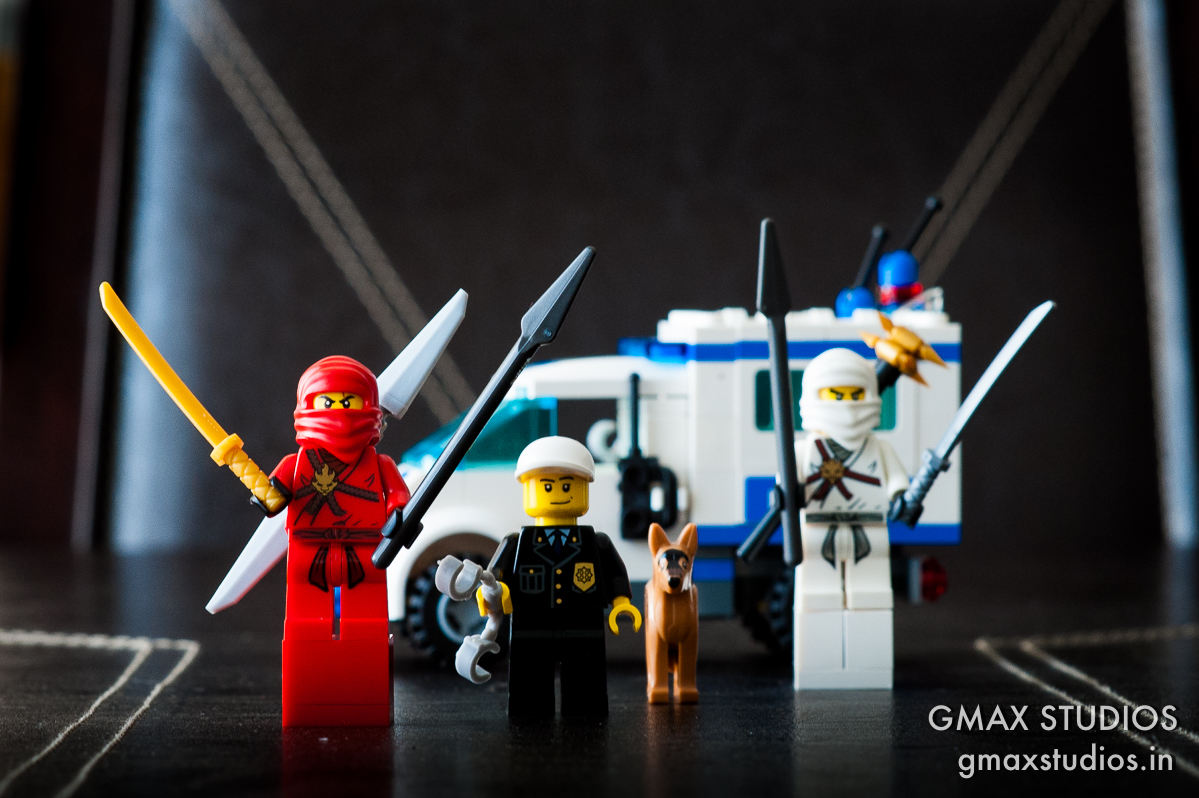


If we make the aperture even smaller by closing it down to f11, the background is almost completely in focus. The eyes of the white Ninja are almost sharp too. You can also make out the form of the chair at the dining table. which was not the case at all when we were shooting at f1.8. Also notice how the stitching on the dining table is in focus BEFORE and AFTER the focus point.
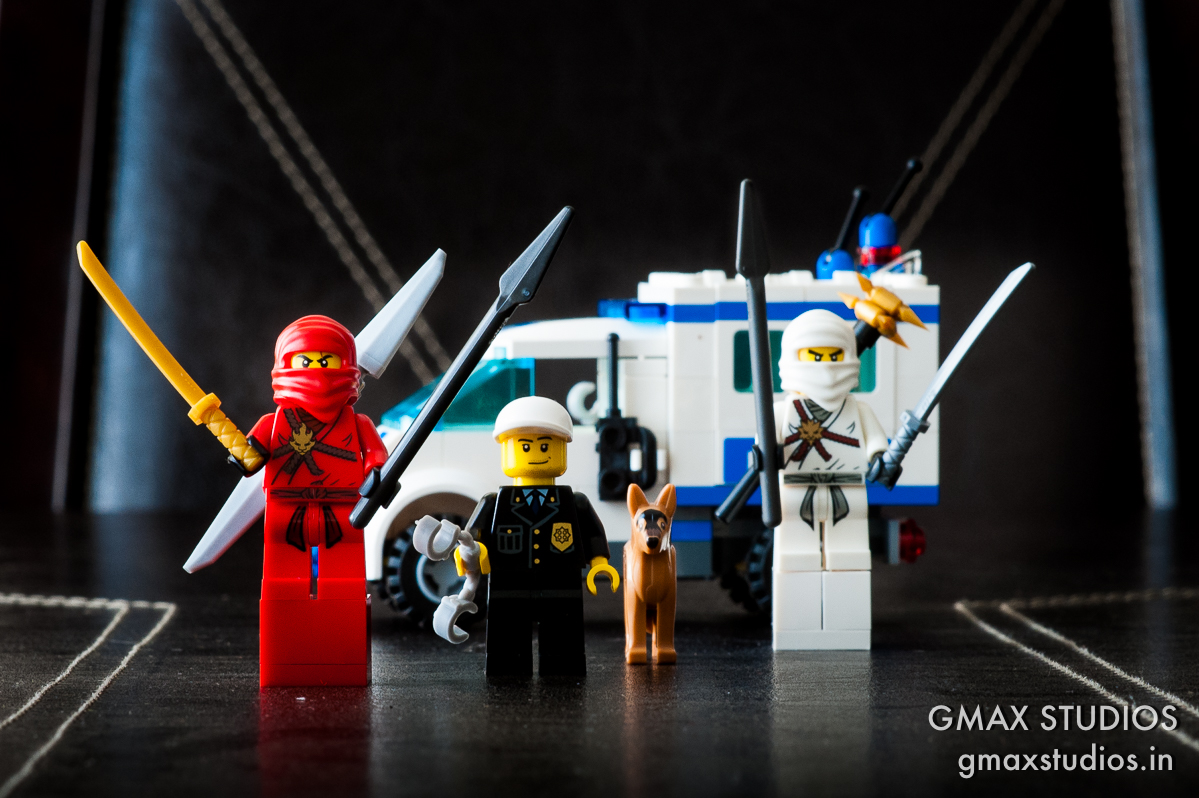

For comparison, here is the first image shot at f1.8 again:

Thumb Rule:
The higher the number of the aperture, more of the background will be in focus. This can be summarised by the graphic below.
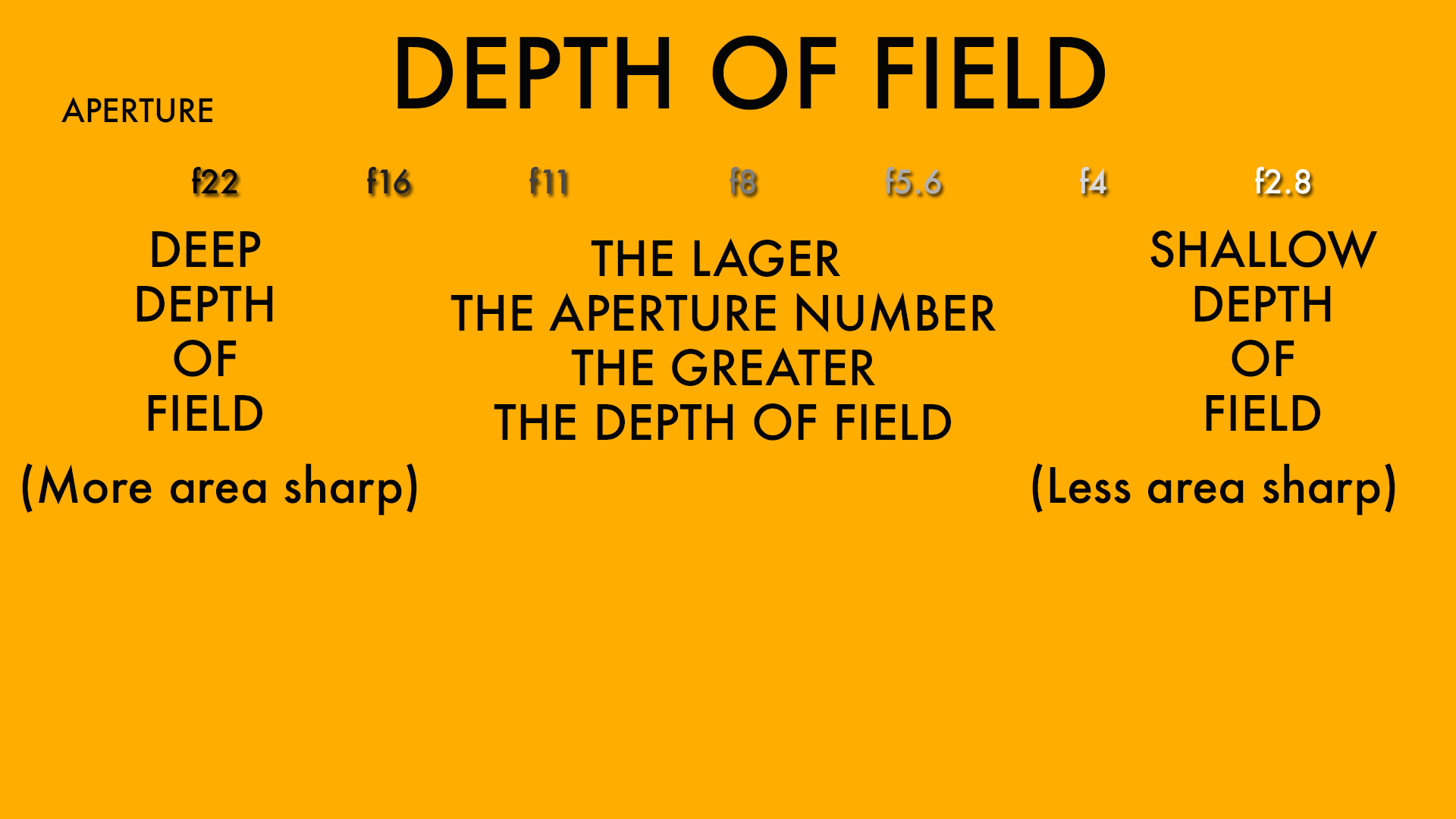
You can download a hi-res version of this graphic to your computer or smartphone by adding us to your Google Plus circles. Also watch the video below to understand this concept better and see a practical demonstration of how aperture affects photos and depth of field. If you like the video, please consider subscribing to our channel by clicking here.
https://youtu.be/q3SvCAlgFLw
Shoot me your questions in the comments or leave your suggestions as to what articles or videos would you like to see next.
Learn photography in one hour
How to restore old photos with 1 click
There are many ways to restore old photos and many complicated ways to do them. Most of them require a lot of patience and understanding of various post-processing techniques and software. In fact, most of them are so complicated that we end up never using them and restoring the old photographs that we want to. But anyway, what I usually do to my pictures is as follows and though "one click" will get you there but it will be almost! Feel free to tweak the settings and sliders as you wish. I have used a normal flatbed scanner which is used to scan documents to scan this photograph. If you use a higher end scanner, your results will be much better. You will need:
- A scanner
- A copy of Adobe Lightroom
If you don't have Lightroom, download it. It comes with a 30 day free trial, so you can use it free and 30 days should be enough for you to correct all your old pictures. But anyway, this is my primary software for all my processing needs so I highly recommend it. Anyway, import your scanned photograph into Lightroom.
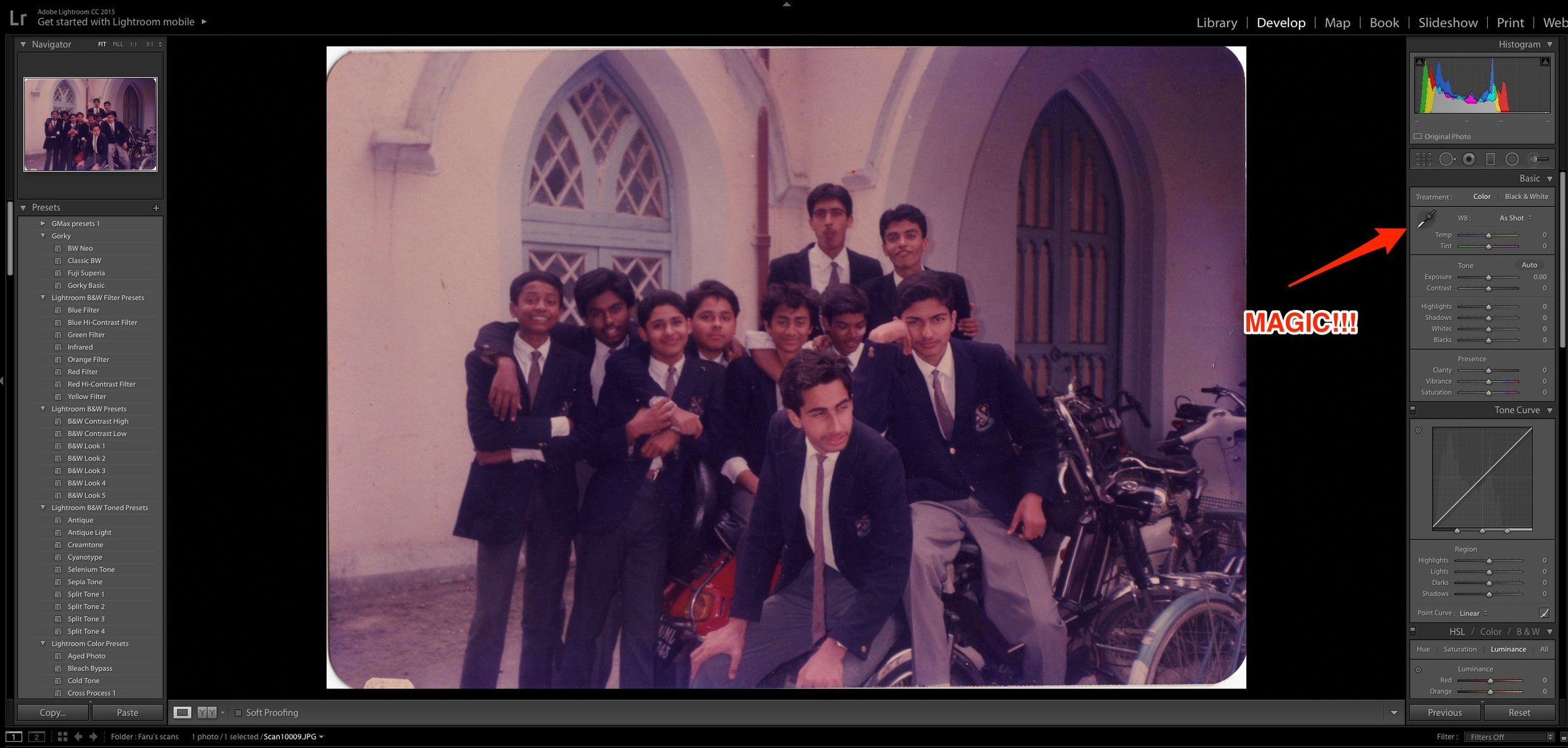
Scanned photograph
Now that magic one click that I was talking about is the one on the top right hand corner.
Select the eyedropper and click on any neutral colour in the photograph. I was lucky that this was a school photo so I could click on the grey trousers that my friends were wearing. Bingo! The software knows which is a neutral colour in the picture and removes the magenta/green cast automatically!
Processed picture
Add some contrast and sharpness and maybe increase the exposure a bit to make the old picture pop. That's it! You are done! Give it a shot! This is what I do to restore my pictures quickly. Here is the comparison.
Also read: How to create a professional white background on any photo in Adobe Lightroom
Do share the pictures that you have restored using this technique. Take look at the video below. Subscribe to our channel by clicking here.
Aperture
Aperture - Learn photography
Imagine in your mind, how the camera works. For you to make a good photograph, a certain amount of light needs to hit the sensor. Let us assume this amount of light to be hundred units. If the light hitting the sensor lesser than the amount of light required, the photographs will be dark or “underexposed”. Similarly, if the amount of light hitting the sensor is more than the amount of light required, the picture will be over-bright or “overexposed”.
There are two ways of controlling the amount of light hitting the sensor-via the aperture or with the shutter speed.
The aperture is nothing but the hole in the lens through which the light enters the camera. For the time being, all you need to know about the aperture is that smaller the number [1.4 or 1.8], the bigger the aperture and similarly, the larger the number will [16 or 22], the smaller the aperture or the size of the hole on the lens. All these numbers are often referred to by using the alphabet F in front of them. So 1.4 is referred to as F1 .4 and 16 is referenced to as F-16. This is just another way of trying to sound cool. There is actually no difference if you say 16 or F-16. Just remember, the smaller the number-the bigger the whole AND the bigger the number, the smaller the pool. This is all that you need to remember about the aperture. This will become second nature as time goes by but it is crucial that for the time being, you remembered this!!!
Adobe Lightroom Tutorial | Professional white background
More than a proper Adobe Lightroom tutorial, this is a quick and dirty tip. When you learn photography and do it commercially for a client - it is often your responsibility to make sure that the client gets the final photograph that he/she wants. At these times, just taking the photograph does not help. You have to go beyond photography and into what we call post-processing.
So, this is more of a photography hack when you don't have all the proper resources, including time, at your disposal. I had to do it once and I realised that I could do it to make my photographs look slightly better and to solve certain problems. By problems I mean, when the purpose of doing this is to create enough contrast so that the subject can be easily cut out from the background and placed in another layout. This is a pretty standard procedure in lots of commercial work done today.
Have you ever felt envious of the way other "professional" photographers manage to shoot their images against a stark white professional looking image? Let us face it - not all of us have a white seamless backdrop at our disposal but that does not mean that we cannot create images that emulate that look. While these may not be perfect but in some cases no one will be able to tell whether you have actually shot them against a white seamless or not. Like all other things, this too depends on how much practice you put into the process and how you fine tune it to suit your own needs.
Also read:
THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO LEARN PHOTOGRAPHY
Well, here is a short Adobe Lightroom tutorial video on how to make your pictures look like they have been shoot against a white seamless backdrop.
This is the first screencast that I have made and I promise that these will get better with time, so please do leave a comment if you would like to see some more. You can subscribe to the channel by clicking here.
Adobe Lightroom Tutorial:
How to restore old photographs in 1 click in Adobe Lightroom
You can visit my personal website and blog here.